Blockchain for Dummies - The five keys to understanding what is Blockchain.
It is highly probable that you have heard the word ‘Blockchain’ during the last year. Even when we all tend to have a vague idea about what it is, the truth is that most of us could not explain why everybody talks about it in every innovation and technology forum.
This article summarizes the most important concepts to understand Blockchain so that you can participate in any conversation about this matter without getting lost in the first sentence. Actually, this article will give you all the information you need to start thinking in your own cases of use for Blockchain. You will learn What is Blockchain, and How Blockchain Works.
Blockchain is Not A Cryptocurrency.
Blockchain is Not A Programming Language.
Blockchain is Not A Cryptographic Codification.
Blockchain is Not An IA Or Machine Learning Technology.
Blockchain is Not A Python Library Or Framework.
It is highly probable that you have heard the word ‘Blockchain’ during the last year. Even when we all tend to have a vague idea about what it is, the truth is that most of us could not explain why everybody talks about it in every innovation and technology forum.
This article summarizes the most important concepts to understand Blockchain so that you can participate in any conversation about this matter without getting lost in the first sentence. Actually, this article will give you all the information you need to start thinking in your own cases of use for Blockchain. You will learn What is Blockchain, and How Blockchain Works.
1. What is Not Blockchain?
Before describing the Blockchain, we will start clarifying what is not Blockchain. Many people misunderstand the terms and concepts, leading to typical mistakes like the followings:Blockchain is Not A Cryptocurrency.
Blockchain is Not A Programming Language.
Blockchain is Not A Cryptographic Codification.
Blockchain is Not An IA Or Machine Learning Technology.
Blockchain is Not A Python Library Or Framework.
“Blockchain is the tech. Bitcoin is merely the first mainstream manifestation of its potential.” — Marc Kenigsberg.
 |
| What is not Blockchain |
2. What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is the name of a whole new technology. As the name states, it is a sequence of blocks or groups of transactions that are chained together and distributed among the users.“The blockchain is an incorruptible digital ledger of economic transactions that can be programmed to record not just financial transactions but virtually everything of value.”– Don & Alex Tapscott.In the end, it works as an immutable record of transactions that do not require to rely on external authority to validate the authenticity and integrity of the data. Transactions are typically economic, but we can store any kind of information in the blocks.
 |
| What is Blockchain |
“Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System” was published by Satoshi Nakamoto back in 2009, and the value of the currency reached its highest historic maximum of $19,783.21 on Dec. 17, 2017. Since that moment, Blockchain has been in the scope of everybody.
3. How Does Blockchain Works?
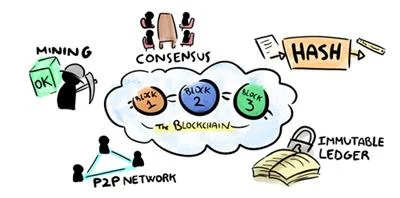
The value of Blockchain technology comes from the distributed security of the system. For this reason, there are several characteristics that are completely necessary for developing or using a Blockchain.We describe the 5 key concepts that are the basis of the Blockchain technology as we know it up to the date, based on the SuperDataScience course for Blockchain:
- Cryptographic Hash
- Immutable Ledger
- P2P Network
- Consensus Protocol
- Block Validation or ‘Mining’
 |
| Five keys to understanding Blockchain |
Cryptographic Hash:
A Hash is a cryptographic function that transforms any input data into a fixed-length string of numbers. Every single input of the hash function will produce a different output, and the result is deterministic: if you use the same input, the output value will be always the same.One of the most important features of the Hash functions is that the conversion is one-way: you cannot reverse the function to generate the original input.
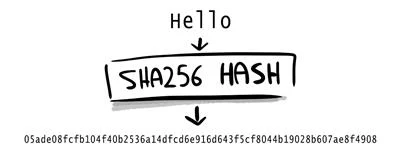 |
| The Hash Function generates a unique code from every different input |
The Blockchain nodes use Hash functions to create a unique identifier of any block of transactions. Every block includes the Hash value of the previous block.
Immutable Ledger:
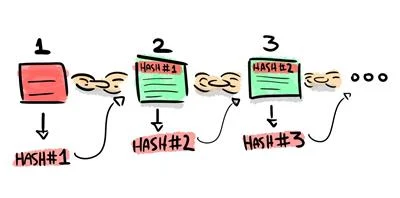
This feature is tightly related to the previous one. Since every block of the chain contains the Hash of the previous one, it is not possible to modify any block without changing the entire chain. Hence, the chain works as an immutable digital ledger.Let us see an example. We have the following chain, in which every block has been hashed and the hash is included in the following one:
If an anonymous attacker removes, adds or modifies any transaction in the first block, the HASH#1 will change:
HASH#1 is included as a part of the contents in Block 2. Because of that, HASH#2 will change too, and the error will propagate to every block of the chain after the block under attack. The user will then declare the chain invalid.
Peer-To-Peer (P2P) Network:
The Blockchain does not need any external or internal trust authority. This is possible because the Blockchain data is distributed among all the users. Every user has its own copy of the transactions and hashed blocks, and they spread the information of any new transaction to the entire network. This way, it is not possible for anyone to alter the information in the chain since it is not stored by an individual entity but for an entire network of node users.Once a block of transactions is validated, it is added to the chain and every user update their local information. Even if an attacker were to modify your local chain, the network will not accept any block from the altered blockchain.
Consensus Protocol Blockchain:
But what is the real blockchain? Users need to meet an agreement about the validity of the chain before adding more blocks.Every time a node adds a new block, all the users have to validate the block by using a common protocol. Typically, the nodes reach a consensus about the correctness of a new block by Proof of Work or Proof of Stake methods.
The nodes check that the new block meets the requisites of their Proof method, including validation for all the transactions inside the block. If the block is valid, they consider it as a part of the Blockchain and keep adding new blocks.
 |
| Every user has its own copy of the Blockchain, and they share any update with the other users |
Block Validation Or ‘Mining’:
This feature is actually not completely necessary for a Blockchain, as we can see with examples like the CREDITS platform. However, is it probably one of the most famous facts about Blockchain thanks to the Bitcoin chain.The term ‘mining’ refers to the act of meeting the Proof of Work requirements for adding a new block with pending transactions to the Blockchain. There are many different mining methods, as they are custom defined for the chain.
The PoW method usually requires the user to create a block with restrictions on its Hash code. Since the Hash code is unpredictable, the ‘miners’ have to test any possible combination before meeting the requirements. These restrictions define the difficulty of the network.
Once a ‘miner’ node finds the solution to the PoW problem, they add the block to the chain and every other node check the validity of the PoW according to their Consensus Protocol. If the block is legit, they will include it on their own local copies of the Blockchain.
3. Conclusions:
Blockchain technology is permanently evolving. However, we can find some key pillars to sustain the added value of this technology.The Blockchain allows users to create a reliable and immutable system for recording any kind of transaction or information. There is no need for an external or internal authority: every user relies on the technology itself, following predefined rules to meet consensus and ensure the integrity and authenticity of the data.
You May Also Like: